Sicherheit
Security Goals
- Confidentiality: protecting data from exposure to unauthorized parties
- Integrity: protecting data from unauthorized modifications
- Availability: Assuring nobody can disturb the system to make it unusable
Adversary Model
- TM that performs arbitrary malicious operations
Protection Domains
- model who can have access to objects like files or devices
- data structure stores
- which objects are mapped to which domains
- level of acces to object this domain has
Data Structures for Protection Domains
- protection matrix #
- each row represents one protection domain | each column represents a object (file, device)
- (-) potentially very sparse entries -> waste of space
- access control lists (ACL)
- list with each object & corresponding access rules for each user
- (+) better use of space
- Capabilites:
- each protection domain has set of capabilites
- capability relatet to object | defines acces to that object
Authentication
The 3 principles for user authentication
- something the user knows
- something the user has
- something the user is
Precomputation Attacks
- ∃ list of already encrypted passwords
- if the encrypted passwords are known, plaintext password can easily be found
Stalted Passwords
- encryption happens with a random number (salt) as additional parameter
- salt stored in plain text along the respective encrypted password
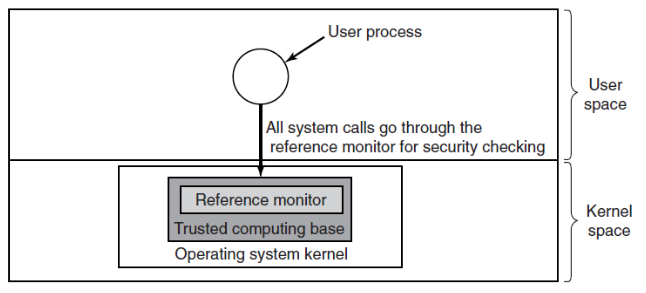
Trusted Computing Base (TCB)
- hardware and software components necessary for enforcing all security rules
- TCB typically consists of
- security-relevant hardware
- parts of OS kernel
- user programs with SU privileges
- OS functionalities that must be part of the TCB
- process creation and switching
- memory management
- part of file and IO management
- reference monitor: central entity checking all security critical system calls
<>
- Discretionary access Control (DAC): System in which users can decide on access rights to objects
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): System enforces mandatory access rules | not modifiably by users
- Bell-LaPadula:
- focus on confidentiality
- users & objects assigned security levels
- simple security property: only read down
- *-property: only write up
=> no information leakage
- Biba:
- focus on integrity
- simple integrity property: only write down
- integrity * property: only read up
Covert Channels
- method of communicating through changed system properies
- modulating CPU usage | locking files
Side-Chanel
- information extracted from implementation of computer system
- cache leakage
- timing information
- power consumption
Malware
- = malicious software
- install backdoors
- take control of machine
- collection of taken over machines -> botnet
- ransomware: encrypt hardware to extort victim
- spyware: steal sensitive information about user | identity theft
- Trojan Horse: malware hidden behind usefull software
- virus: program that reproduces by attaching itself to antother program
- virus payload may only execute after time or sufficion spread of virus
- worm: can spread independently over network (no host needed)
- use explot to gain acces
- use bootstrap or loader to download actual worm
IoT Malware
- Malware targetting IoT devices
- scan internet to find vulnerable IoT devices
Code Injection vs. Code Reuse
- code Injection: adding new node to Control Flow Graph (CFG)
- code Reuse: Adding new path to CFG
Data Execution Prevention (DEP)
- prefents execution of memory region a program can write to
=> separation of data and text
Hybrid Exploits
- use of both code injection and code reuse
Return-into-libc Attacks
- workaround in systems with DEP
- redirects execution to security critical functions ins shared libraries (e.g., UNIX C library libc)
- libc linked to almost every unix program
- (-) attacker relies on functions available in library
- (-) attacker can only invoke one function at a time | no conditional branching

